An article from The Academy of Finland
Nudity sparks the brain
The naked truth: our brains process nude pictures more efficiently than pictures of clothed people, new Finnish study reveals.
Scientists have come some way toward figuring out why we love nude pictures. Brain imaging studies have localised areas in the brain that are specialised in detecting human bodies in the environment.
But so far it no-one has found out whether the brain processes nude and clothed bodies in different ways – until now.
Researchers at the University of Tampere and the Aalto University, Finland, have shown that the perception of nude bodies is boosted at an earlier stage of visual processing than the perception of clothed bodies.
Brain prefers us in the nude
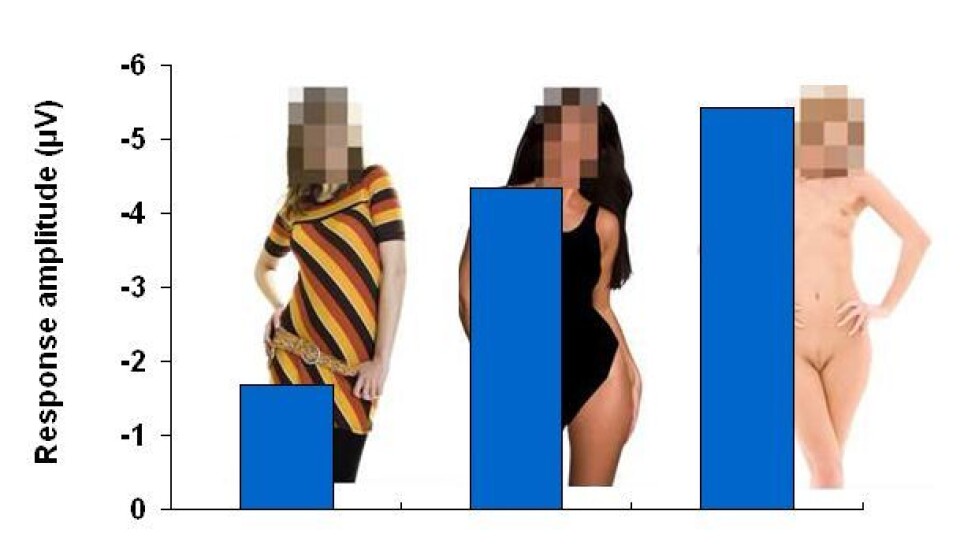
In the study, participants were shown pictures of men and women. The models wore either normal everyday clothes or swimsuits, or were nude. Visual brain responses were recorded from the participants' electrical brain activity, enabling the researchers to investigate the early stages of visual information processing.
The results showed that in less than 0.2 seconds the brain shows improved efficiency when processing pictures of nude bodies than when the person in the picture is wearing clothes.
In fact, the less clothing the models in the pictures were wearing, the more enhanced the information processing: the brain responses were at their strongest when the participants looked at pictures of nude bodies, second strongest when looking at bodies in swimsuits, and weakest when looking at fully clothed bodies.
Male brains more selective
Male participants' brain responses were stronger to nude female than to nude male bodies, whereas the female participants' brain responses were not affected by the sex of the bodies shown.
The results show that the brain boosts the processing of sexually arousing signals.
Subjective impressions confirmed brain reactions
In addition to the brain responses, the participants' self-evaluations and measurements reflecting the activation of the autonomic nervous system were in line with expectations, showing that nude pictures were more arousing than the other types of pictures.
Such fast processing of sexual signals may play a role in reproduction, and it ensures efficient perception of potential mating partners in the environment, says head researcher Jari Hietanen of the University of Tampere.






